 In this episode of NPR’s Science Friday podcast from last year, New York Times columnist Randy Stross talks about how we’re now entering an age where our digital “products” are no longer ours to own.
In this episode of NPR’s Science Friday podcast from last year, New York Times columnist Randy Stross talks about how we’re now entering an age where our digital “products” are no longer ours to own.
When you buy music as an MP3 (assuming it’s not protected) you can copy or transfer it freely, to be used as wish, just as cassette tape recordings used to be. But in a world of controlled devices such as the Kindle or Apple’s iPod and iPad devices, it’s no longer to separate the “product” (be it an app, an e-book or an interactive website) from the device you use to consume it. Companies now have the ability to change the content, the experience or your access, after you have purchased it. Sometimes the content will be hosted online, in the cloud, which means you can access it anyway, but you’ll also never truly possess it.
Should we just accept this change, and be happy we won’t be carrying our media around for the rest of our life in shoeboxes, or should we fight to hold onto our rights of ownership so that we can be free to watch, read and listen whenever and however we want?
Read more, or listen to the MP3.
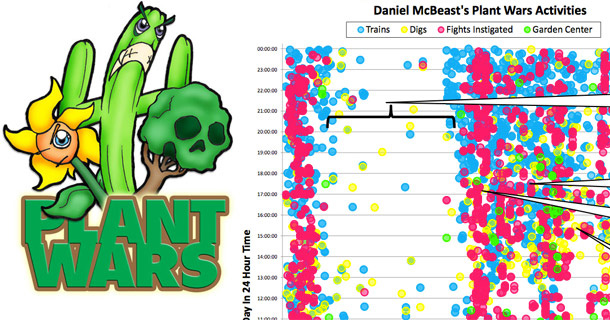
Image credit: draggin on Flickr.















 @
@








 Like all images on the site, the topic icons are based on images used under Creative Commons or in the public domain. Originals can be found from the following links. Thanks to
Like all images on the site, the topic icons are based on images used under Creative Commons or in the public domain. Originals can be found from the following links. Thanks to